Does Gum Disease Prevent Me from Getting Implants?
Understanding Gum Disease
Gum disease, or periodontal disease, is an infection of the gums that is primarily caused by the buildup of bacterial plaque. This condition is not only the leading cause of tooth loss in adults but is also linked to serious health issues like heart attacks, strokes, and coronary artery disease. The impact of gum disease on oral health is profound; it can lead to tooth and bone loss, and significantly compromise the integrity of the gums, increasing the risk of infection around dental implants and potentially leading to implant failure. Fortunately, gum disease can be effectively treated through methods such as deep cleanings, antibiotics, and even surgery, emphasizing the importance of preventive care to maintain healthy teeth and gums. It is crucial to treat gum disease before undergoing major dental procedures such as dental implants to ensure successful implant treatment.
How Does Gum Disease Affect Oral Health?
Gum disease, or periodontal disease, significantly impacts oral health in several detrimental ways:
- Tooth Loss: One of the most severe outcomes of untreated gum disease is tooth loss, due to the destruction of the supporting tissue and bone structures of the teeth.
- Bone Loss: As gum disease progresses, the bones that support the teeth can become infected and gradually deteriorate. This loss of bone can lead to tooth mobility and eventual tooth loss.
- Infection and Inflammation: The bacteria causing gum disease can lead to persistent inflammation of the gums, which may cause them to become red, swollen, and prone to bleeding during brushing or flossing.
- Impact on Dental Implants: Existing gum disease can jeopardize the success of dental implants. The inflammation and infection can spread to the area around the implant, potentially leading to implant failure. If you develop gum disease after having dental implants, it can impact the jawbone, remaining teeth, and overall implant quality.
- Overall Health Risks: Gum disease has been linked to other health issues, including heart disease, diabetes, and respiratory conditions, due to the inflammatory processes associated with chronic periodontal infection.
Can Gum Disease be Treated?
Gum disease, or periodontal disease, can be treated effectively through a variety of methods depending on the severity:
- Deep Cleaning: This includes scaling to remove tartar from above and below the gum line, and root planing to smooth out the roots and help the gums reattach to the teeth.
- Medications: Antibiotics in the form of mouth rinses or gels applied directly to the gum pockets may be used to reduce bacteria and inflammation.
- Surgery: In severe cases, procedures like flap surgery (for reducing the gum pockets), bone grafts (to regenerate lost bone), or soft tissue grafts (to cover exposed roots) may be necessary. It is important to allow gums to heal after gum surgery before getting dental implants, as this ensures a strong and healthy foundation for the implant.
- Laser Therapy: This modern treatment uses lasers to remove infected gum tissue and promote healing.
- Improved Oral Hygiene: Regular brushing, flossing, and dental check-ups are crucial. Using an antimicrobial mouthwash can also help reduce bacteria.
- Lifestyle Changes: Quitting smoking and maintaining a healthy diet are important to improve treatment outcomes and prevent the disease from worsening.
Early intervention is key to managing gum disease effectively, so regular dental visits are essential for maintaining oral health.
Impact of Gum Disease on Dental Implants
How Gum Disease Affects Dental Implant Success
The success of dental implants heavily depends on the condition of the gums and jawbone. Addressing gum disease before the dental implant treatment is crucial, as gum disease can inflame and weaken gum tissue, significantly increasing the likelihood of implant failure. In fact, active gum disease generally disqualifies a patient from being a candidate for dental implants due to the associated risks. Furthermore, bone loss—a common consequence of advanced gum disease—can make it challenging to securely anchor dental implants.
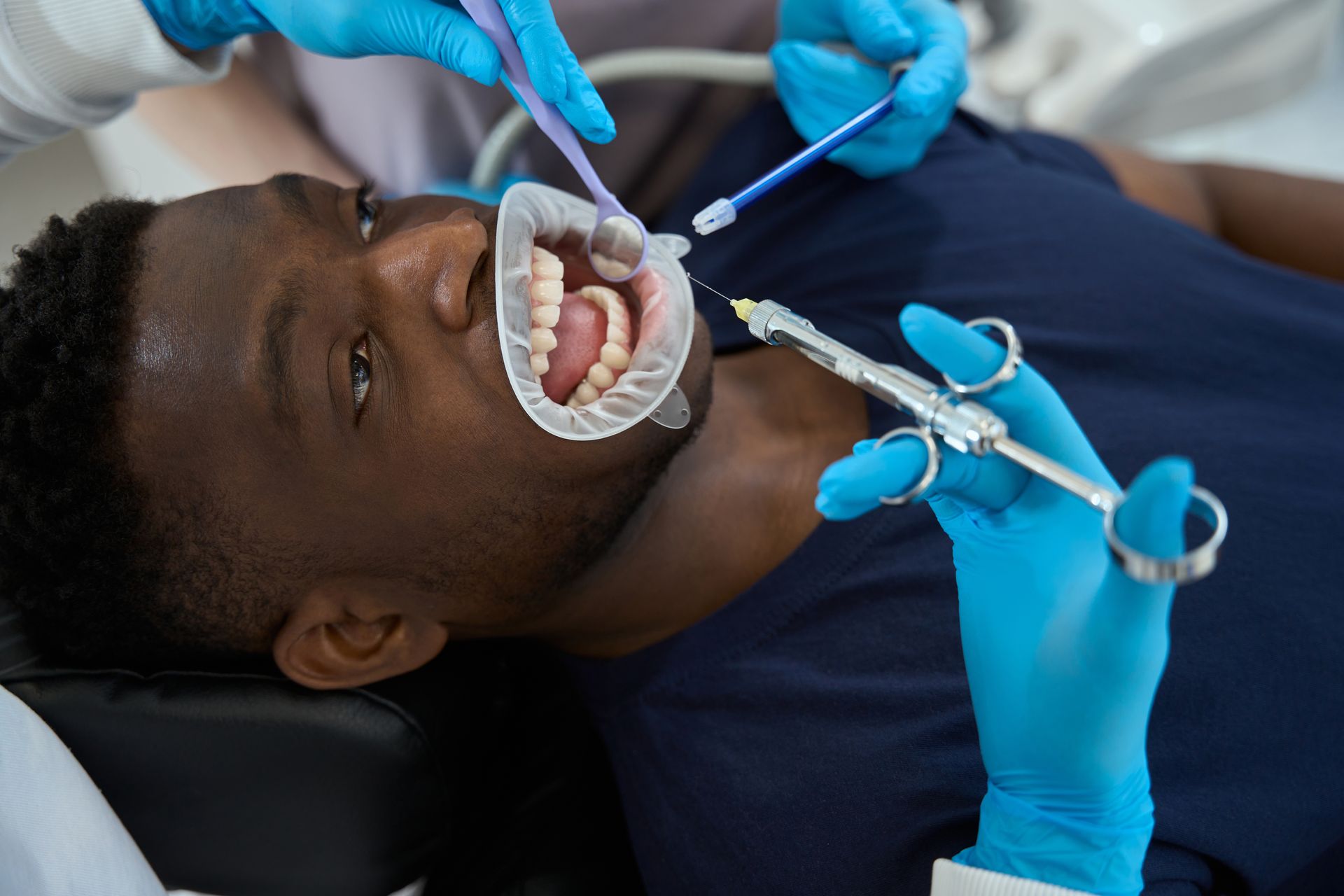
Bone Loss and Dental Implant Candidacy
- Bone loss can make it difficult to support dental implants.
- Healthy gums and bone density are necessary for dental implant success.
A bone graft can be used to strengthen the jawbone, creating a better base for dental implant
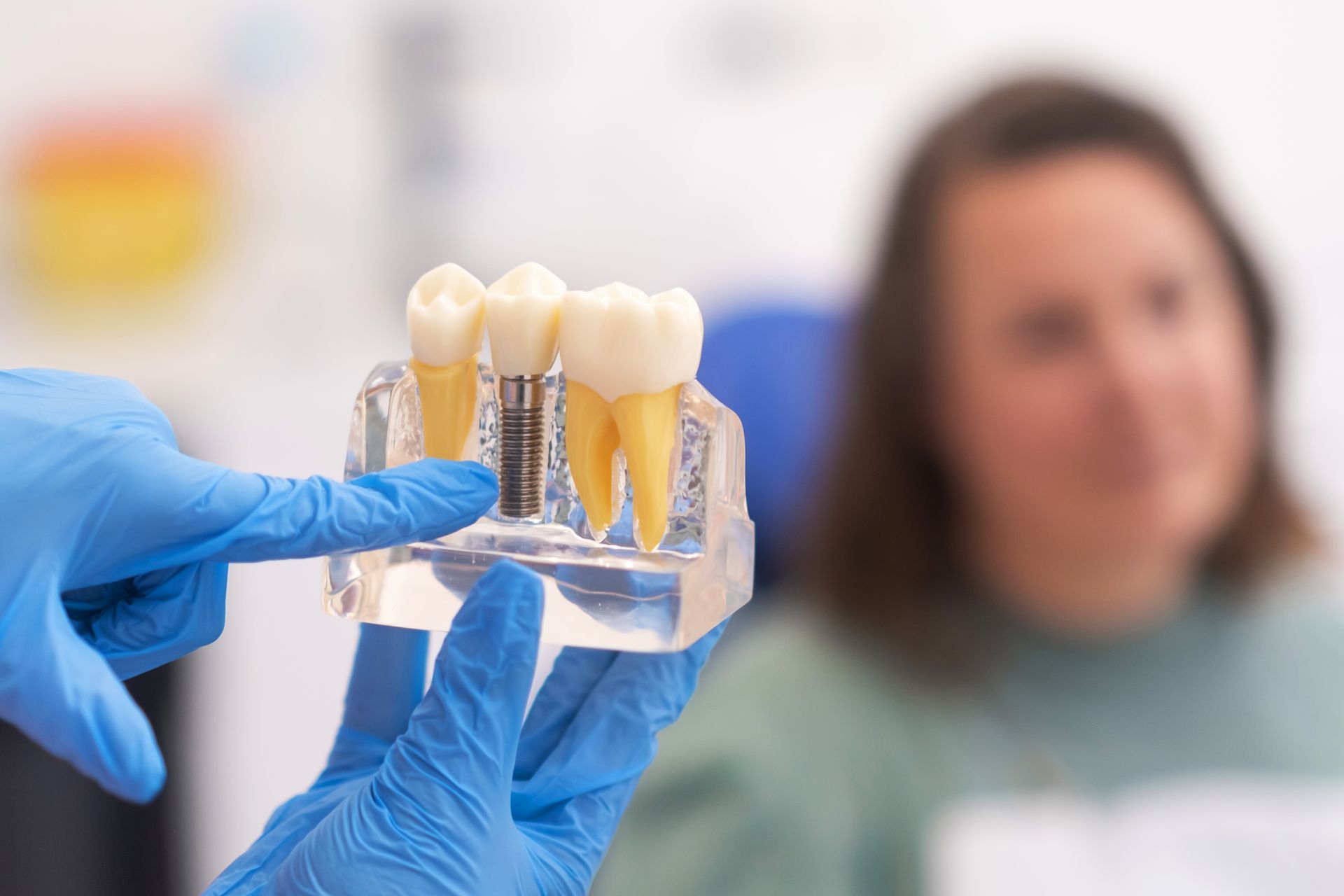
Dental Implant Candidacy
Requirements for Dental Implant Surgery
To be considered for dental implant surgery, candidates must exhibit good oral hygiene and have healthy gums. Sufficient healthy bone density to support the implant is also critical. Those who suffer from poor oral hygiene, inadequate bone density, or certain systemic health issues may not be suitable for dental implants. Additionally, there is a risk of developing gum disease, specifically peri-implantitis, after getting a dental implant.
Who Is Not Suitable for Dental Implants?
People with poor oral hygiene, inadequate jawbone density, or certain medical conditions may not be suitable candidates for dental implants.
Preparing for Dental Implants with Gum Disease
Tips for Gum Disease Prevention and Management
- Preventing gum disease is crucial for maintaining healthy teeth and gums.
- Simple preventative measures to prevent gum disease include regular brushing and flossing, and regular dental check-ups.
The Dental Implant Procedure
Dental implant surgery involves the placement of an implant that acts as a new root for the tooth. Gum disease can impact the ability to replace missing teeth with dental implants by causing significant bone loss, which may necessitate additional procedures like bone grafting or sinus lift surgery. This implant is typically topped with a crown, bridge, or other dental restoration to mimic the appearance and function of natural teeth. However, potential risks such as infection and nerve damage should be considered and discussed with a dental professional.
Risks of Dental Implant Surgery
Dental implant surgery is highly successful, but like all surgeries, it carries some risks. These include:
- Infection at the implant site: Proper hygiene and post-operative care are crucial to minimize this risk.
- Nerve damage: This can result in pain, numbness, or tingling in the teeth, gums, lips, or chin.
- Sinus problems: Implants in the upper jaw can protrude into the sinus cavities, causing complications.
- Implant failure: Smoking, poor oral hygiene, or insufficient bone density can lead to the failure of the implant to integrate with the jawbone properly.
How Much Does a Dental Implant Cost?
The cost of dental implants can vary widely, with traditional implants ranging from $1,500 to $3,000 per implant, and mini implants costing between $1,000 and $2,000. Not all insurance plans cover dental implants, so it's important to verify what is included in your specific policy.
Importance of Consulting a Dentist or Specialist for Dental Implants with Gum Disease
If you have gum disease and are considering dental implants, consulting with a dentist or specialist is crucial. They can assess the impact of gum disease on your eligibility for implants and help devise an appropriate treatment plan. Dental implants offer a functional and aesthetic replacement for lost teeth, but the success significantly depends on the health of your gums and underlying bone. Prioritizing gum health not only enhances your eligibility for such procedures but also contributes to your overall well-being.